Chinese scientists have achieved 99.99% lithium recovery using amino acids and miniature batteries, a groundbreaking and environmentally friendly approach.
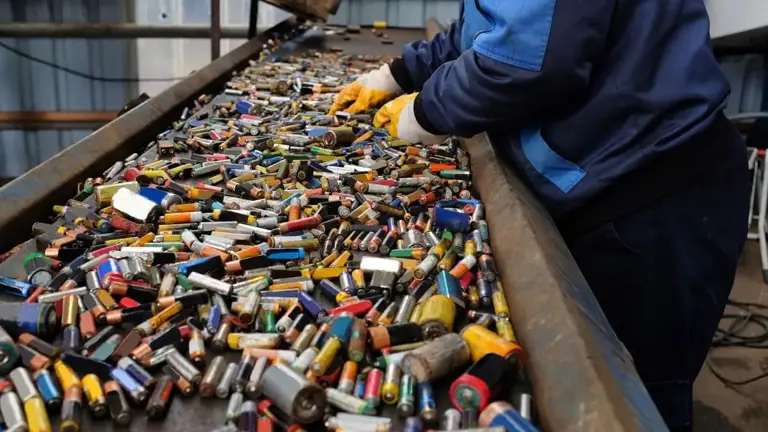

Lithium-ion batteries power our daily lives, from smartphones to electric vehicles. However, as demand grows, so does the problem of e-waste.
Waste batteries release toxic chemicals that pollute soil and water, while mining fresh lithium and other metals depletes natural resources and harms ecosystems.
To address these issues, a team of Chinese researchers has developed a safer and more sustainable recycling method that eliminates the need for harsh acids by using a neutral solution.
A safer way to extract metals
Used lithium-ion batteries contain valuable metals such as lithium, nickel, cobalt, and manganese that can be reused in new batteries.
Most current recycling methods use strong acids or ammonia to extract these metals, but these processes can harm the environment.
Developed by scientists at Central South University in Changsha, Guizhou Normal University, and the National Engineering Research Center for Advanced Energy Storage Materials, the new method works at a neutral pH, reducing pollution and safety risks.
To achieve this, the researchers combined two innovative ideas: using tiny “miniature batteries” to break down the battery material, and adding the amino acid glycine to help extract the metal.
These tips can recover valuable metals without the use of harsh chemicals.
The critical role of amino acids in sustainable cycling
Glycine is a common amino acid that plays a vital role in this method.
It acts as a binder, trapping metal ions such as lithium, nickel, cobalt, and manganese, preventing them from forming unwanted by-products.
In addition, glycine is a natural buffer that keeps the solution at a neutral pH, making the process much safer than traditional acid-based recovery techniques.
But here’s the real surprise: the glycine solution left over after metal extraction is not a waste product – it’s a resource.
It does not produce toxic by-products, but can be reused as fertilizer, transforming chemical waste into beneficial agricultural products.
This means that glycine not only optimizes metal recycling, but also ensures that every part of the process contributes to sustainability.
Micro batteries help in breaking down old batteries
A key finding of this new method is the creation of tiny “miniature batteries” in the recycling solution.
This helps to break down the waste battery material, making it much easier to extract the metal.
The researchers mixed old battery pellets with iron(II) salts, sodium oxalate, and glycine in a neutral liquid.
This forms a thin layer of iron(II) oxalate on the particles, which acts as the anode and the battery material as the cathode.
This setup triggers a reaction in which iron(II) is converted to iron(III) and oxygen ions in the battery material are converted to hydroxide (OH-) ions.
This reaction destroys the structure of the battery, causing lithium, nickel, cobalt, and manganese to dissolve in solution. Not only is the process fast and effective, but it also eliminates hazardous waste.
The efficiency of battery recycling is amazing
The results of this approach are impressive.
In just 15 minutes, it extracts 99.99% lithium, 96.8% nickel, 92.35% cobalt, and 90.59% manganese from used batteries.
What are the real highlights? The remaining glycine solution can be used as fertilizer, further reducing waste.
This new recycling method is not limited to recycling metals; It’s about doing it in a way that further protects the planet.
It provides a smarter, safer, and more sustainable approach to battery recycling, ensuring that we make the most of our resources while minimizing harm to the environment.
The study was published in the journal Anji Wonder Chemical International.

 Entering China
Entering China